Enabling Real Time Collaboration feature in Datahub#
The Guide has moved!
The information on this website may be outdated as of July 2025. Please view the new curriculum guide located at https://curriculum-guide.datahub.berkeley.edu/
Real-Time Collaboration in Jupyter is one of the most requested functionalities, which has also proven to be a complex use case to develop. A little bit of context about RTC, It was previously deployed as part of the Stat 159 hub during Spring 22. However, we found severe data corruption issues which led to disabling RTC. Many issues were fixed as part of the jupyter_collaboration package which is an extension that enables RTC in the latest Jupyter Lab 4 version. However, a subset of users in the Data 100 SU 23 course were affected with random error messages (snapshotted below) which went away after disabling the jupyter_collaboration package.
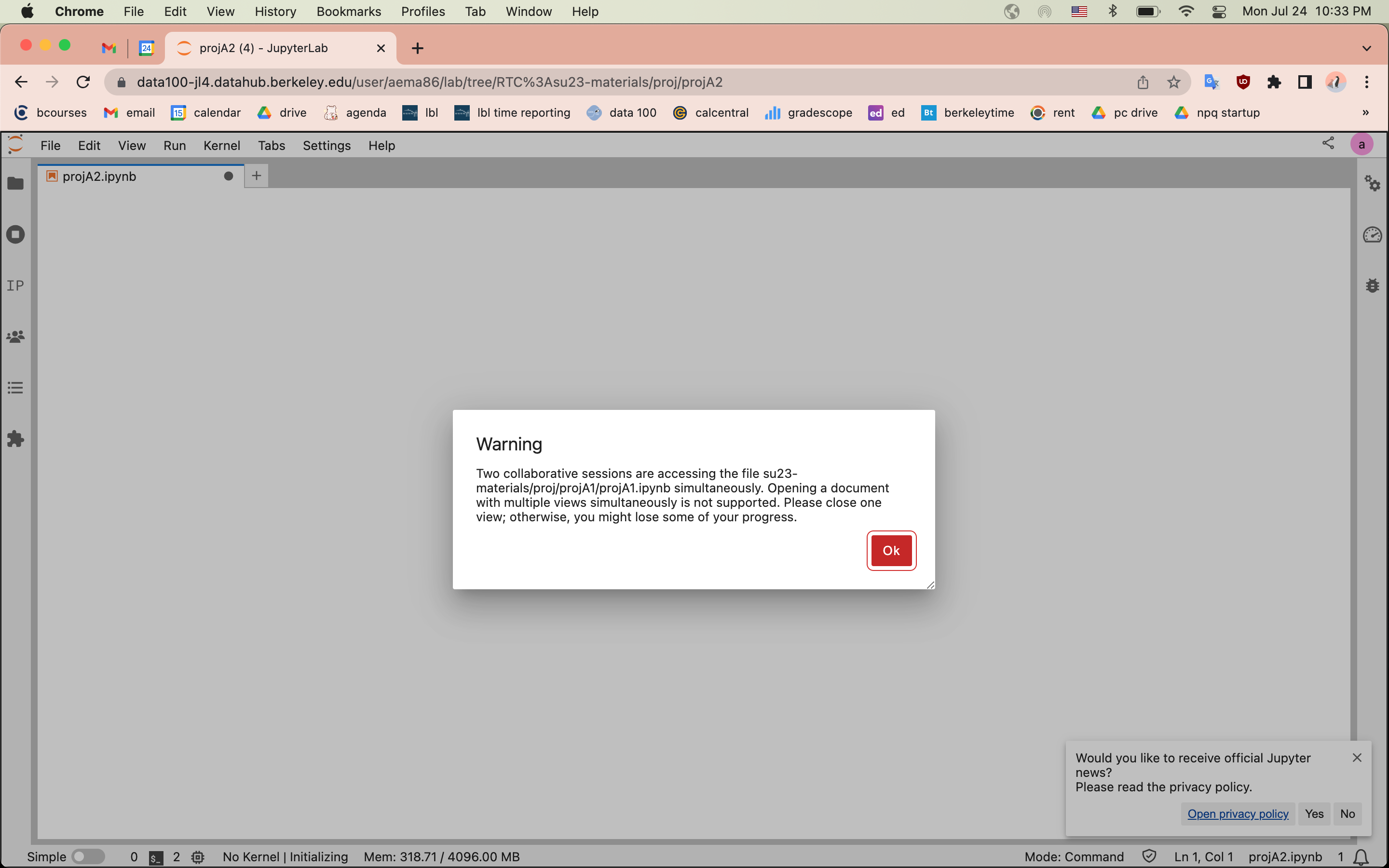
Fig. 9 Here is a random error message received by Data 100 users#
Note
RTC feature is still in a testing stage. New bugs get uncovered and are also fixed immediately
Note
Please do keep in mind that if you as an instructor wants to distribute links to students enrolled in your course then you should consider generating and distributing links through nbgitpuller pathway. However, If you are considering usecase around students working collaboratively using Jupyter notebooks then consider RTC.
We are looking for instructors who are interested to pilot RTC in their course setting. If you are interested in enabling RTC functionality then please do make a github request. Do keep in mind that you are deploying an early-stage bleeding edge version of RTC and are open to the possibility that hub stability and/or data integrity could get impacted by this decision.
Note
Data considerations for adopting RTC!
User notebooks were corrupted in RTC hosted hub. You can refer to the details here.
Security considerations for adopting RTC!
If a user shares a link with another user, They can modify all the files in the owner’s home directory for the specific hub, including other assignments and homework.
When a user who owns the notebook stops the server, then the validity of the shared link expires - either explicitly from the control panel or after non-activity for 60 minutes.
There is no option for the notebook owner to revoke the link, but they can stop the server, which makes the shared link invalid.
Anyone can forward the generated link to the next person as there is no link-level user control. Users would have to be careful where they share links while that server is active since anyone on the internet could gain control.
An user who has access to the shared link needs to leave the current session to go and work on their files.
Steps to enable RTC#
You can start collaborating with others by following the below steps,
Step 1#
Open your IPython (ipynb) notebook files in Jupyter Lab interface. If you are unsure how to generate a nbgitpuller link to access your notebook in Jupyter Lab or Retro Lab interfaces, Please install this plugin in the Mozilla Firefox browser, which will walk you through the steps required to generate the link for the file easily.
Note
Please do keep in mind that Real-Time Collaboration(RTC) functionality is not enabled in classic notebook and retro lab interfaces!
Step 2#
As a next step, Generate the shareable link to be shared with your collaborators. Follow the below steps to generate this link,
In the Menu bar, Click on the Share option (option next to Help).
Select “Share Jupyter Server Link” which opens a prompt a the centre of the screen that shows an option to copy the shareable link.
Select “Copy Link” option which copies the link to your clipboard
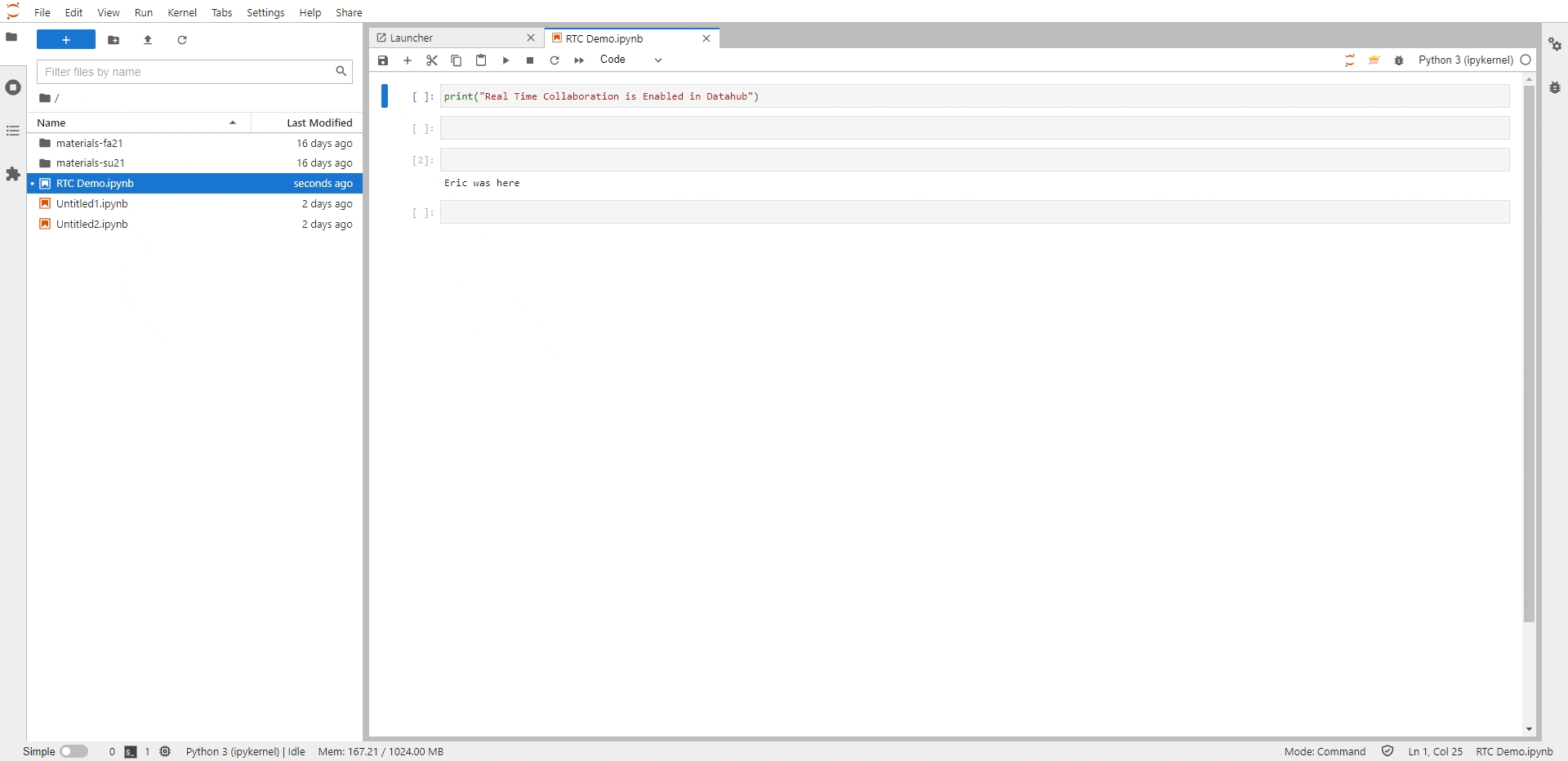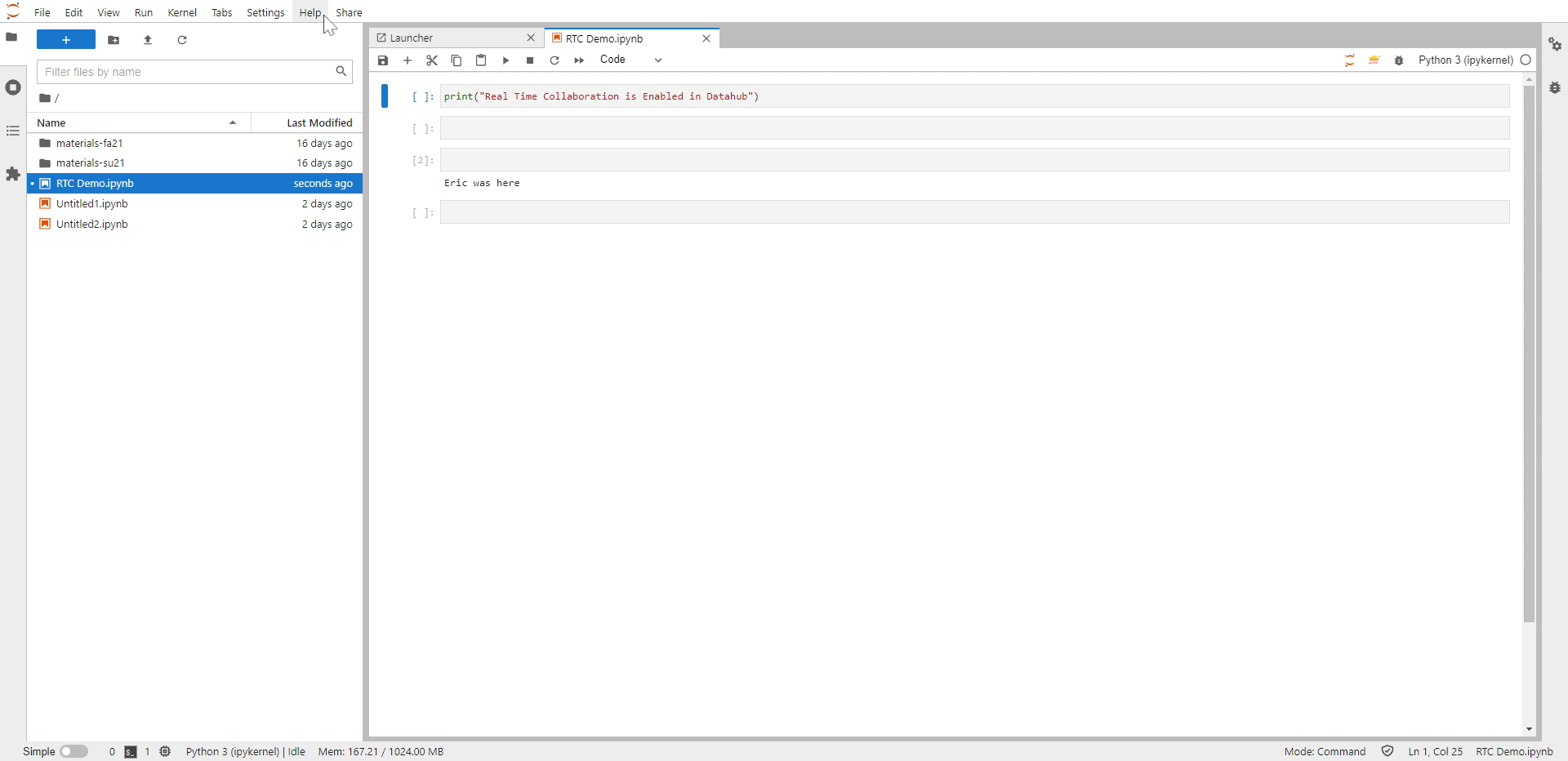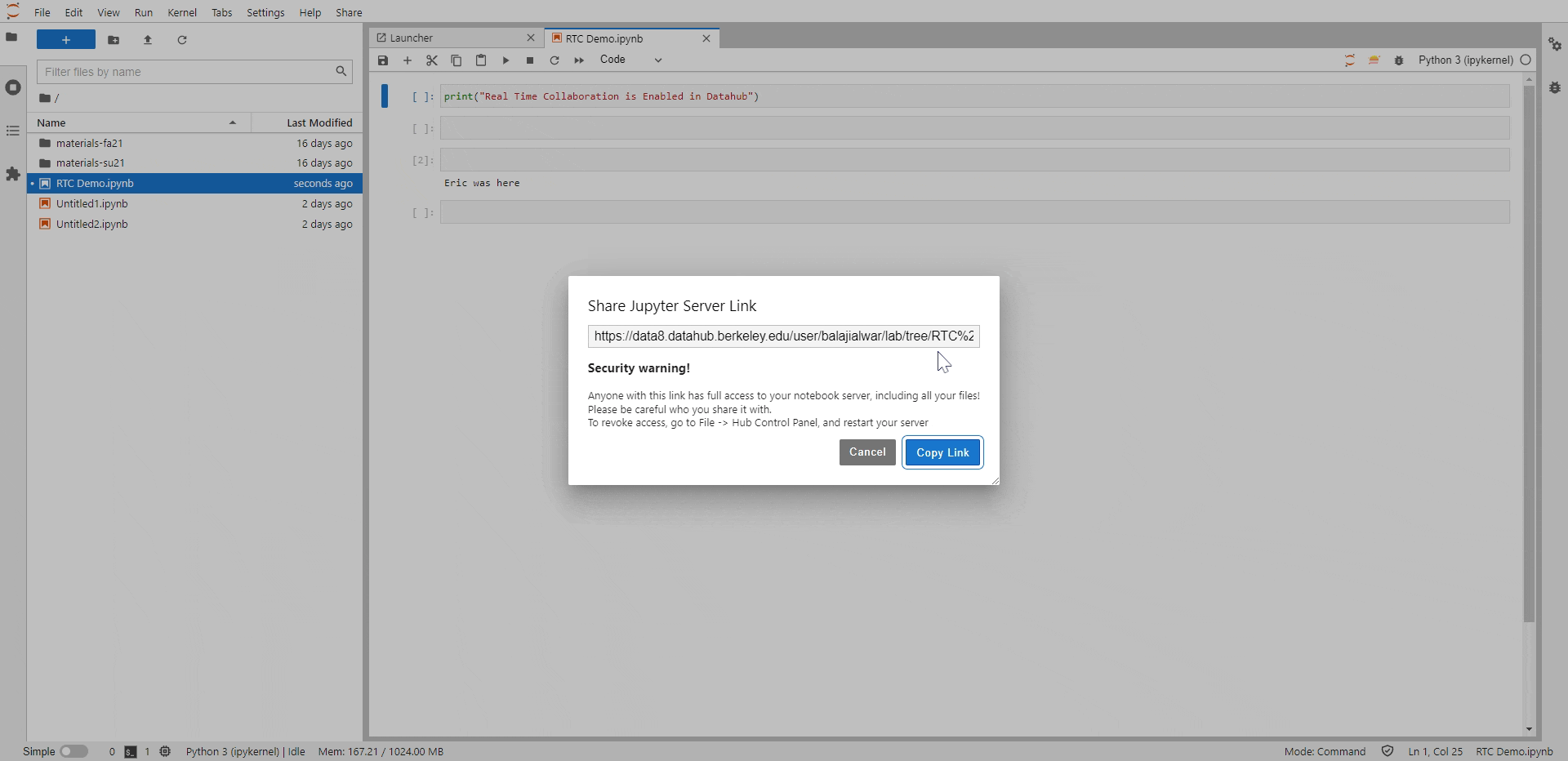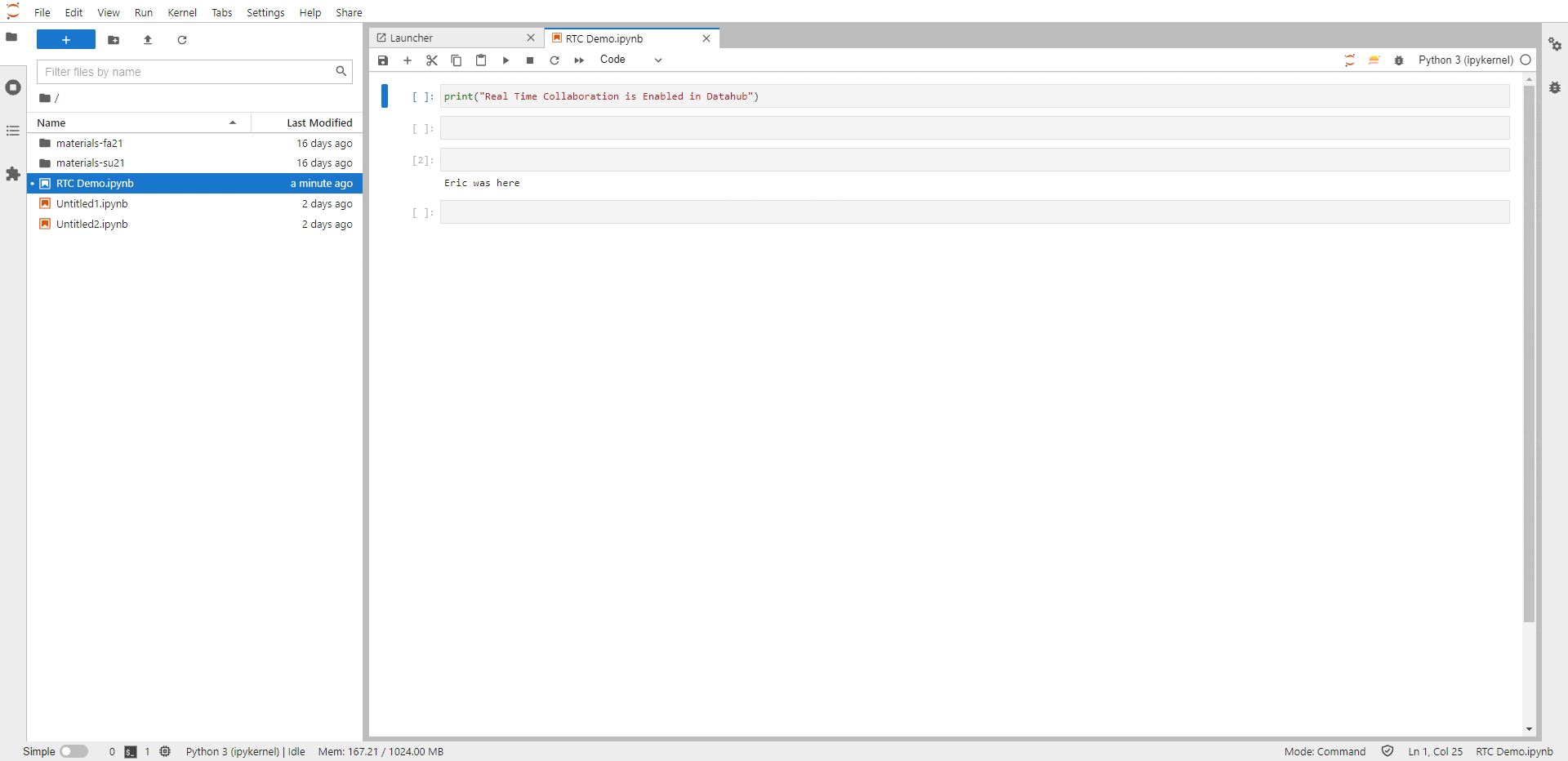
Fig. 10 Here is how you can generate a shareable link#
Step 3#
Share this link with your collaborators. They will be able to access your notebooks immediately and make edits to the notebook in real-tim You can also see the cursors from other users with an anonymous username, a username that will disappear in a few seconds to make room for what is essential, the document’s content.
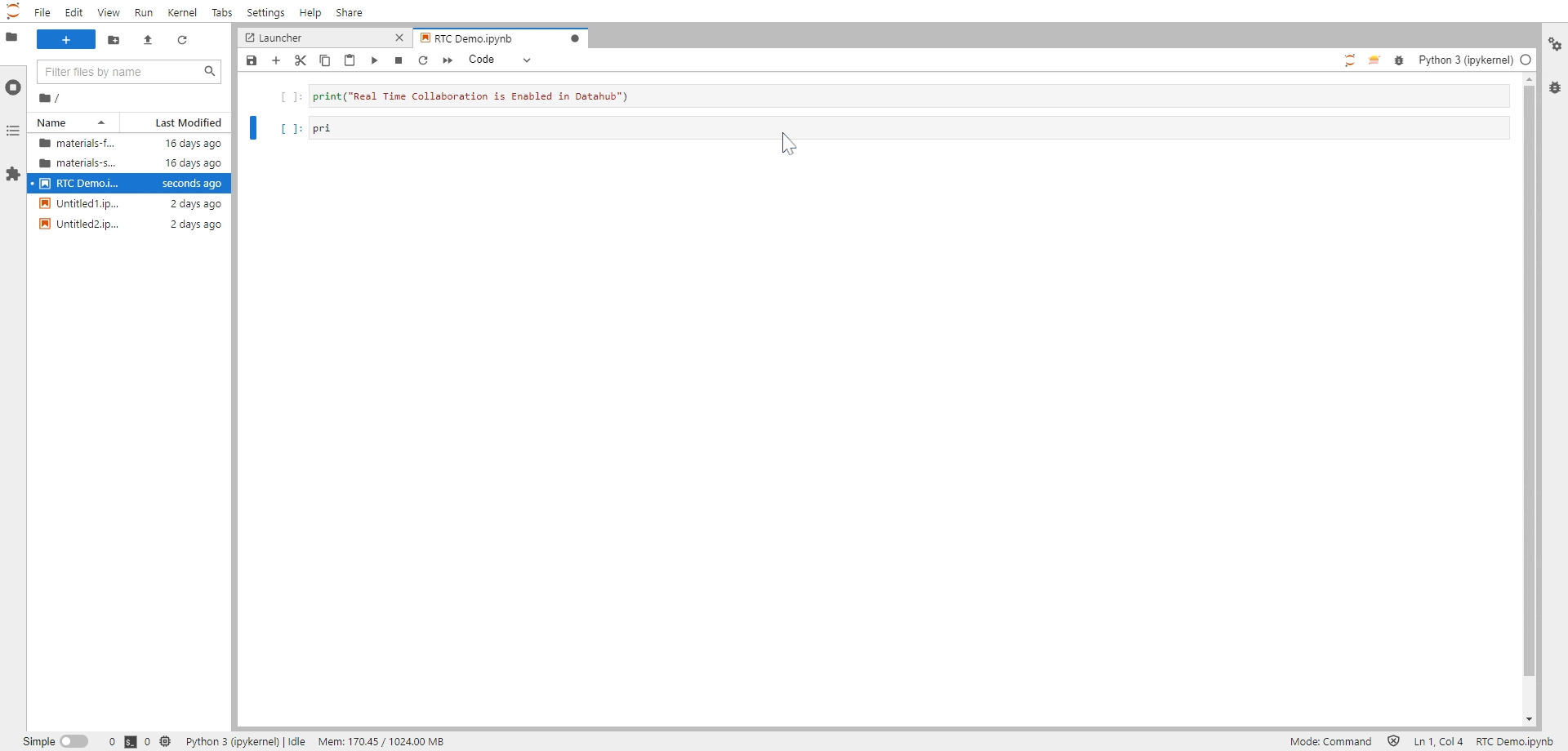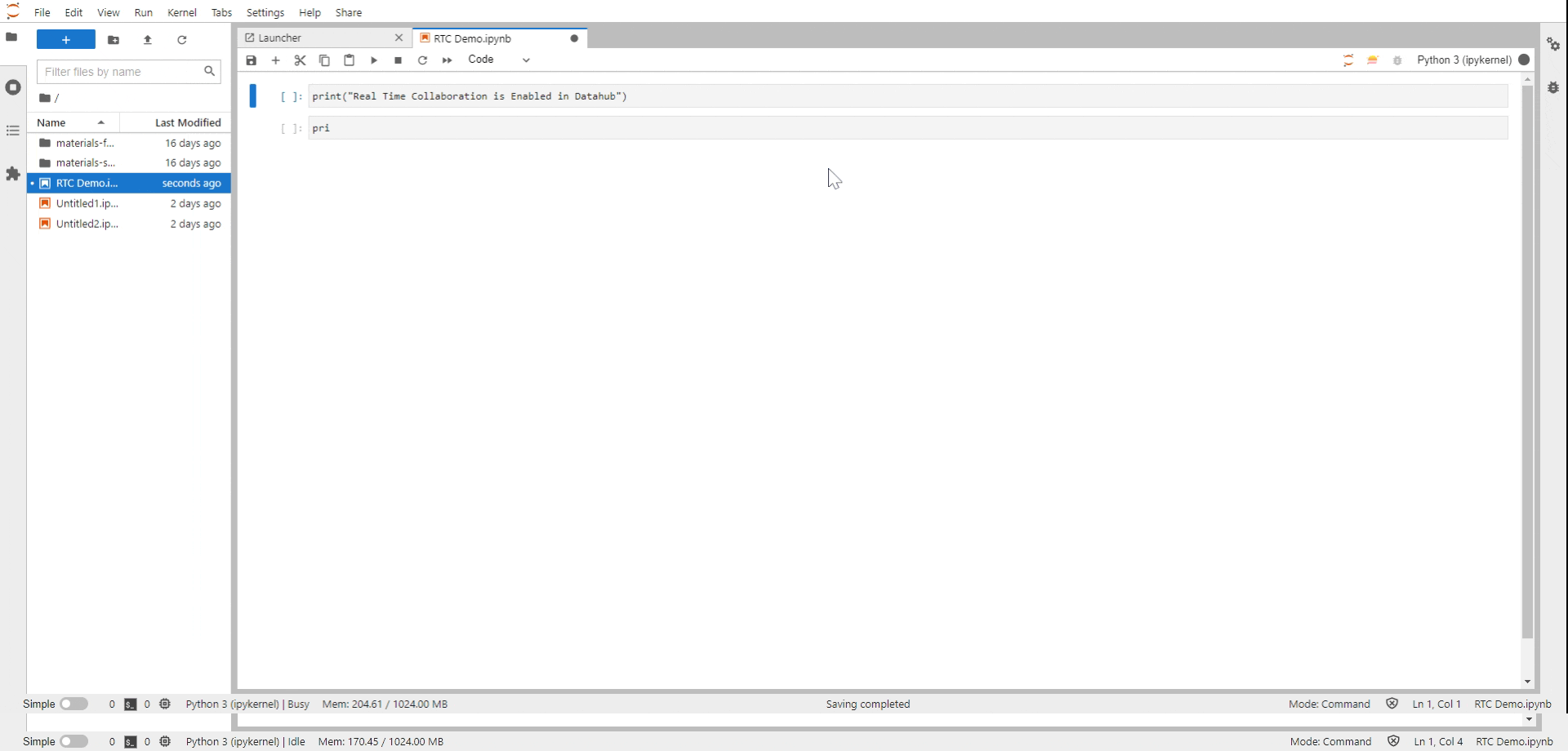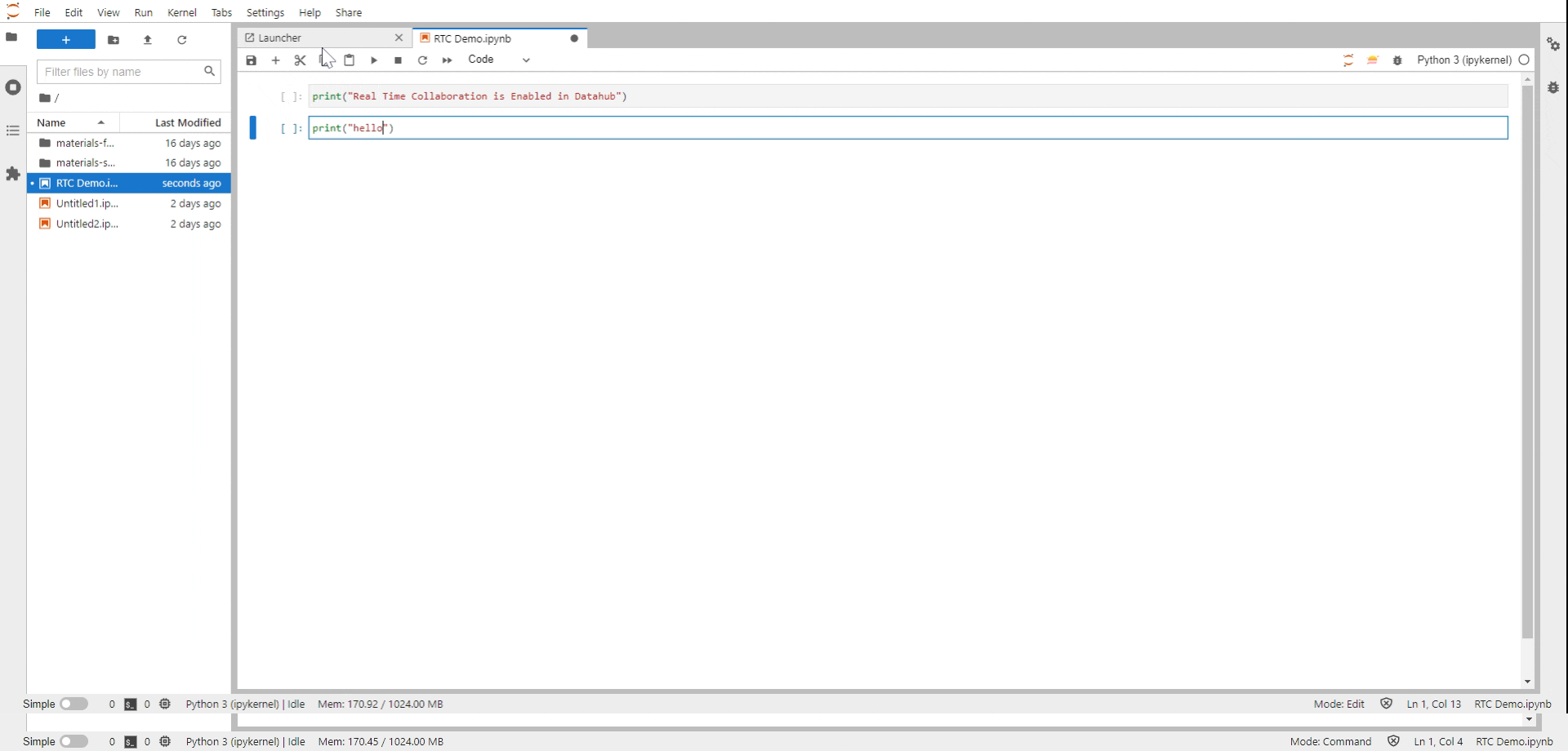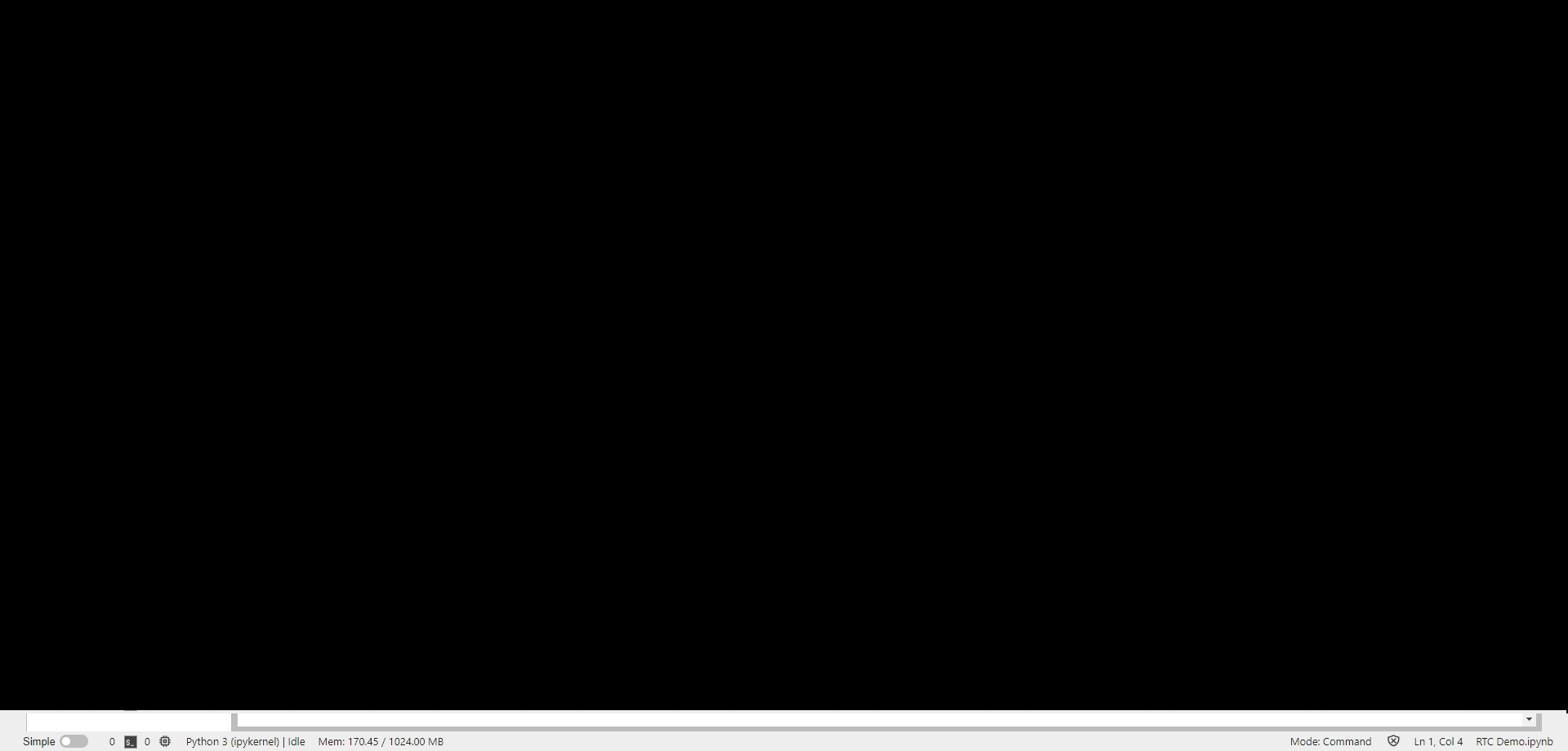
Fig. 11 Real Time Collaboration (RTC) in action#
If you are interested to learn more about how real time collaboration works in Jupyter Lab, do refer to this documentation If you are interested to get under the hood of real time collaboration and understand the framework enabling the shared data type, do refer to this documentation
